Unable to Send Email?
Frustrating, I know.
Being unable to send an email can ruin your workday, wreck productivity, or even worse cause you to lose out on an valuable opportunity.
Fixing email delivery issues is one of the top three things we do for our server management customers. We even provide email blacklist monitoring services to provide alert them to email blacklist issue. But if you are not blacklisted, you can save yourself some money by checking these five items before opening a support ticket.
- Bad Passwords
- Network Connection Errors
- ISP Blocks & Email Ports
- SMTP Authentication Settings
- SSL Connection Settings
1. Bad Passwords
Never ASSUME, because when you ASSUME, you make an ASS of U and ME. — Jerry Belson
An incorrect password sounds simple, but many support tickets we see turn out to be simple password issues. People complain they are unable to send an email and just assume the password is correct.
We reset the password and bang — email is flowing again.
I think the problem often stems from extra spaces. Firefox and other applications often add spaces to copy and pasted passwords. To be sure you are not picking up spaces, paste the password to your address or search box in your web browser. You can then quickly see if there are extra spaces.
When in doubt, always try resetting your password first.
2. Network Connection Errors
Sometimes mail servers crash — not often but I see it happen on WHM/cPanel and Plesk servers. Simply restarting the service from the control panel often fixes the issue.
Your email client should return a connection error.
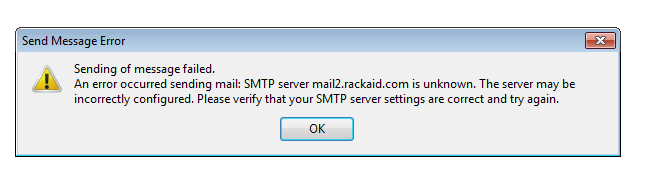
The clue in this message is “mail2.rackaid.com is unknown.”
The error could be a general network issue, and you may want to try again in a few minutes. If the issue persists, you could have a DNS issue. If DNS is not working, you cannot send emails. Of course, it could be something simple – like an incorrectly spelled domain name.
If you change your DNS, keep in mind the change must propagate. Some ISPs can take 24-48 hours to update their DNS. In the meantime, you may want to try connecting to the IP address.
You can use intodns.com to check for DNS issues.
3. ISP Blocking Port 25
Your ISP is blocking port 25. Port 25 is the default SMTP port. Technically, you should be using port 587. Port 587 is the default mail submission port according to the RFC, but in practice, people use port 25.
Many ISPs force you to use their own SMTP servers even if you have your own. U-verse, Spectrum and Comcast often block port 25 by default. I even see this on business accounts.
You can use telnet to test if your ISP blocks port 25.
[jeffh@office ~]$ telnet mail.rackaid.com 25 Trying 54.221.232.71...
This test hangs until it times out. To confirm our ISP is blocking port 25, you need to run a local test on your server. SSH to your server and then run the same test.
telnet mail.rackaid.com 25 Trying 54.221.232.71... Connected to mail.rackaid.com. Escape character is '^]'. 220 mail.rackaid.com ESMTP Postfix
If you see the STMP banner, you know your server’s SMTP server is working, either a local firewall or your ISP is blocking access.
One tip is to use port 587. Many ISPs do not block this port:
[jeffh@office ~]$ telnet mail.rackaid.com 587 Trying 54.221.232.71... Connected to mail.rackaid.com. Escape character is '^]'. 220 mail.rackaid.com ESMTP Postfix
If port 587 also fails, call your network provider. On most business accounts, they will open either port 25 or 587. Increasingly, ISPs require residential accounts use their SMTP servers.
For reference, here are the email ports to keep in mind:
- IMAP 443
- IMAP over SSL 993
- POP3 110
- POP3 over SSL 995
- SMTP 25
- SMTP over SSL 465
- SMTP Submission Port 587
4. SMTP Authentication
Most SMTP servers require a valid username and login to send emails. If your SMTP authentication settings are incorrect, you should see an error similar to this one:
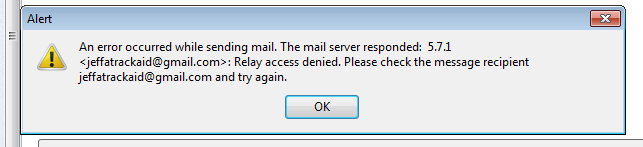
Most email clients have two critical settings:
- Authentication Method
- Connection Security
The authentication defines the type of password system your email client uses to contact the server. In most cases, this is Normal, Plain, or Encrypted.
The connection security method refers to network security between your email client and the server. Typically, this is None, STARTTTLS, or SSL.
The authentication method and connection security methods must be correct. Usually, if your server requires SSL (or STARTTLS), you should select a Plain password. A plain password sounds insecure, but it is not. You are sending the plain, unencrypted password over an encrypted network, so t is safe.
5. SSL/STARTTLS Connections
For security, many email service providers require you to connect to SMTP over a secure connection. SMTPS or secure SMTP uses TLS/SSL to secure the network connection between your email client and the server. In 2008, I called for ending clear text protocols on this very site.
I recommend you always use SSL/TLS. In fact, the Electronic Frontier Foundation runs STARTTLS Everywhere in an effort to promote better email security.
(When I mention SSL, you could also be using TLS. TLS is the newer variety of SSL; however, many older email servers still use SSL protocols.)
There are two methods used for security email with SSL.
- Implicit SSL
- TLS On-Demand (STARTTLS)
Port 465 usually requires you to use SSL. The mail server assumes your email client will communicate over an SSL-secured network link. Trying to connect without SSL wll fail.
STARTTLS may work with both port 25 and 587. Essentially, your email client connects over an insecure network connection and then asks the server to upgrade the connect to a secure one. Despite having TLS in the name, STARTTLS doesn’t mean TLS will be used. Both SSL and TLS are acceptable protocols for securing the communication. Your email client and the server negotiate a secure network connection.
Summary
These are the major reasons we see for being unable to send email. If you are having issues, please contact your email service provider for support. If you operate a Linux-based email server and need help, check our our Email Support Services.

